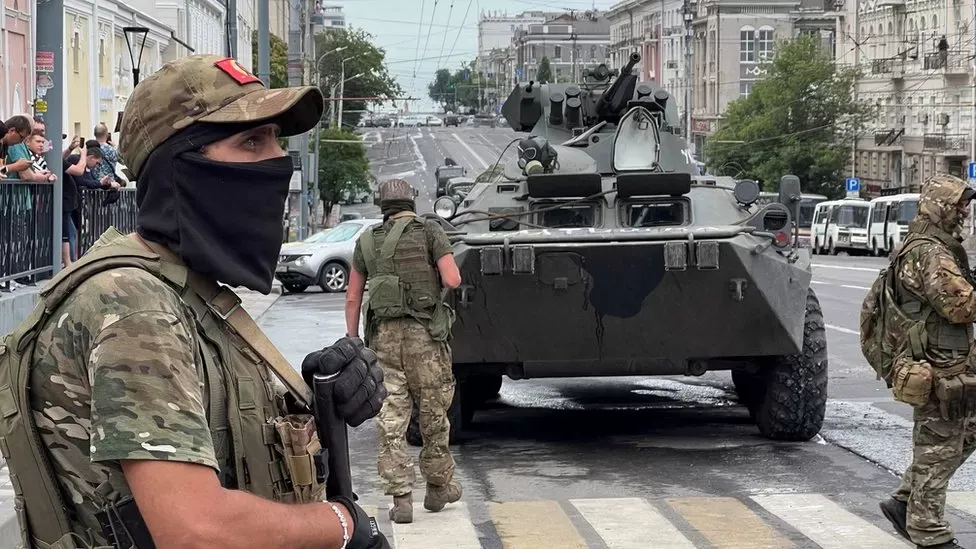
DeepSeek Sparks Online Frenzy: China’s AI Moment?
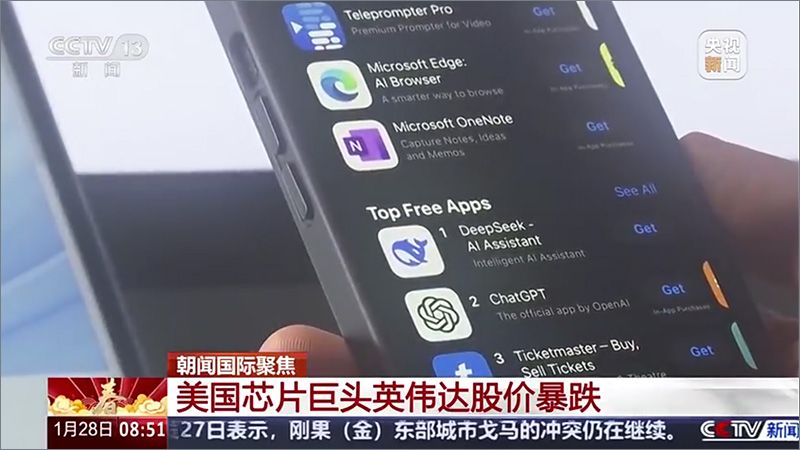
DeepSeek, a Chinese artificial intelligence startup, has quickly risen to prominence in the global AI landscape, drawing attention from both domestic and international audiences. Its emergence has sparked intense discussion across Chinese social media and traditional media channels, with users debating its significance and potential impact on the AI industry.
WNM has been tracking online conversations in China to understand public reactions to DeepSeek’s development, as well as how the technology is being framed in national discourse. While the model has gained traction in global media, Chinese discussions emphasize its role as an alternative to AI models developed in the United States, positioning it as a potential challenger to dominant Western players like OpenAI.
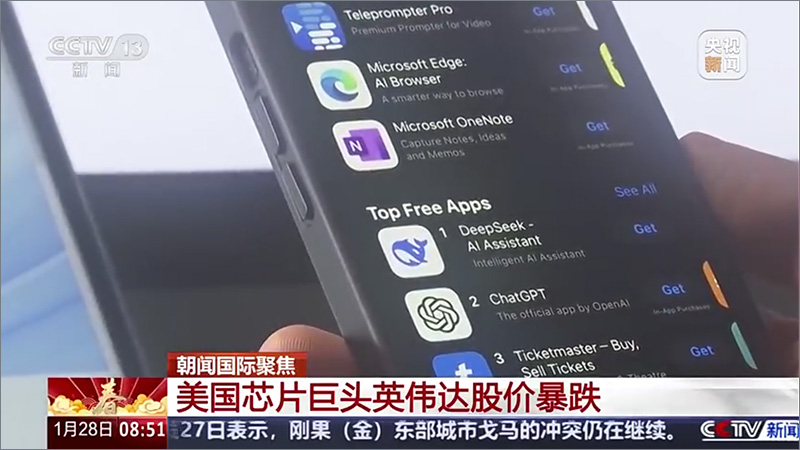
Chinese media reports highlight DeepSeek’s innovative approach, portraying it as a serious competitor to OpenAI’s GPT-4. Analysts within China suggest that the company’s advancements have raised concerns among U.S. tech firms, which have traditionally maintained a dominant position in AI development. The discussion extends beyond technical performance, with many commentators framing DeepSeek’s success as a reflection of China’s growing influence in cutting-edge technology and an indication of shifting global power dynamics.
On Chinese social media platforms, users have primarily focused on the model’s features, sharing memes and personal experiences with DeepSeek’s capabilities. However, some discussions have touched on the broader geopolitical implications, noting how AI innovation has become an increasingly competitive field between China and the United States.
One of the most widely discussed aspects of DeepSeek, according to Chinese media, is its cost efficiency. Reports suggest that OpenAI invested an estimated $100 million to train GPT-4, while DeepSeek reportedly achieved comparable performance with an investment of less than $6 million. Operational costs also appear to be significantly lower, with DeepSeek’s R1 model reportedly costing just $2.20 per million words, compared to OpenAI’s $60 per million words.
Chinese analysts attribute this cost advantage to a unique training methodology that optimizes data processing rather than relying on vast computing power. Unlike U.S. companies that heavily invest in GPU-based infrastructure, DeepSeek is said to use a more streamlined algorithmic approach, allowing it to achieve efficiency while maintaining performance.
According to discussions in Chinese technology media, DeepSeek’s rise has unsettled major U.S. tech companies. Reports suggest that companies such as Meta, which have invested heavily in their Llama models, are reassessing their strategies in response to DeepSeek’s lower-cost development approach. Some Chinese commentators have pointed to this as an indication that the traditional correlation between financial investment and AI performance may no longer hold.

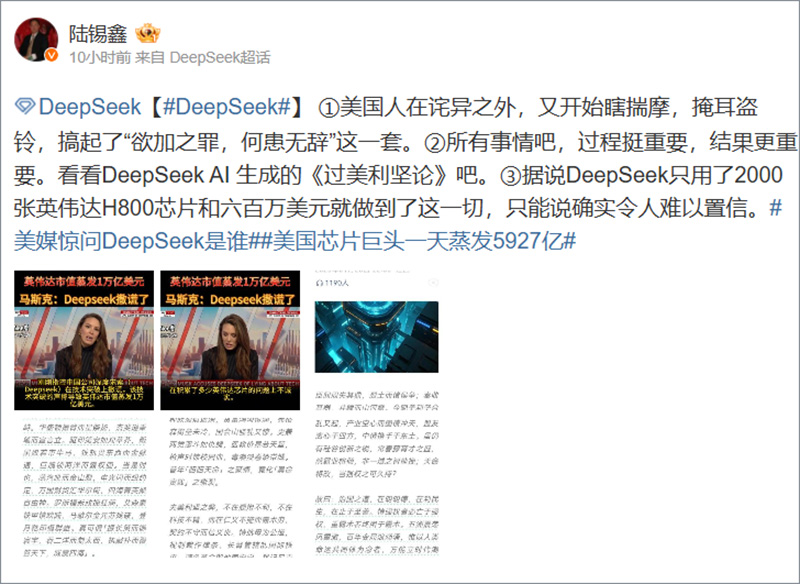
Financial reports from Chinese sources have also linked DeepSeek’s emergence to a sharp market reaction in the United States. It has been widely reported that Nvidia’s stock saw a steep decline of 16.86% in a single day, erasing $594 billion in market value, while the Nasdaq index fell by 3.07%. While these figures have been debated, many Chinese analysts interpret them as signs of investor uncertainty in the face of growing competition from Chinese AI firms.
DeepSeek’s decision to open-source some of its technology has further fueled discussion in China. According to Chinese media, the company’s latest release, Janus-Pro-7B, includes multimodal capabilities that some reports claim outperform Western counterparts in key benchmarks. Many Chinese commentators view the decision to open-source as a bold move that contrasts with the more guarded, proprietary strategies of U.S. AI companies.
Beyond the technical and economic implications, DeepSeek’s success has also sparked deeper philosophical discussions in China. A widely circulated AI-generated essay titled On the Rigidity and Fragility of America has gained traction on social media, drawing historical parallels between past empires and what some Chinese analysts describe as internal contradictions within the United States. The essay, referenced in Chinese discussions, argues that while the U.S. remains a global power, its social divisions, economic inequalities, and involvement in overseas conflicts may signal an eventual decline.
Many online commentators in China have engaged with these ideas, interpreting them as part of a broader historical trend in which no global leader remains unchallenged indefinitely. This perspective has been echoed in various media discussions, where DeepSeek’s rise is framed not just as a technological achievement but as part of a larger narrative in which China is increasingly shaping the future of AI.
On January 28, shortly after DeepSeek’s emergence in international headlines, reports surfaced that the company’s website had come under cyberattack. Chinese media sources have claimed that the attacks originated from U.S.-based IP addresses, with some commentators interpreting this as a sign of growing rivalry between the two countries in the field of artificial intelligence and cybersecurity.

According to Chinese commentators and analysts, DeepSeek’s rapid rise represents more than just a technological milestone—it is a moment of reflection on China’s growing role in global AI development. While U.S. firms have traditionally led the field with substantial investments, DeepSeek’s ability to achieve competitive performance at a fraction of the cost is seen by many in China as a challenge to long-standing Western dominance in artificial intelligence.
As global tech firms react to DeepSeek’s ascent, discussions in China increasingly frame the development as part of a broader shift in AI power dynamics. Whether DeepSeek will maintain its momentum remains to be seen, but within China, the company’s success is widely viewed as a sign of the country’s expanding influence in the AI revolution.
More from the author


